The Importance of Play in Learning and Development
- Kitteeh

- Dec 25, 2025
- 3 min read
Play is often seen as just a way for children to pass time, but it holds a much deeper role in learning and development. It shapes how children understand the world, develop skills, and build relationships. This post explores why play matters and how it supports growth in meaningful ways.
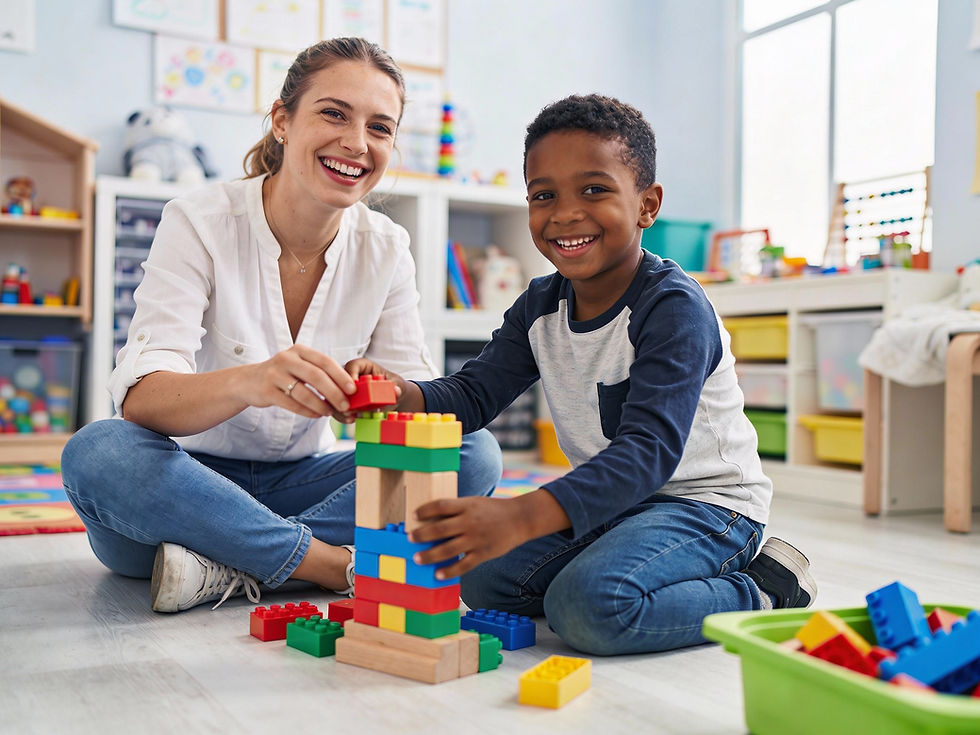

How Play Builds Cognitive Skills
Play encourages children to think creatively and solve problems. When kids engage in pretend play or build with blocks, they practice planning, experimenting, and adapting. These activities help develop critical thinking and reasoning skills that are essential for learning.
For example, a child building a tower with blocks learns about balance and gravity without formal instruction. They test ideas, see what works, and adjust their approach. This hands-on experience strengthens their understanding of cause and effect.
Play Supports Emotional and Social Growth
Through play, children learn to manage emotions and interact with others. Group games teach sharing, cooperation, and conflict resolution. Role-playing helps children express feelings and understand different perspectives.
Imagine a group of children playing “store.” They take turns being the cashier and the customer, negotiating prices and practicing polite conversation. These moments build empathy and communication skills that last a lifetime.
Physical Development Through Active Play
Active play, such as running, climbing, or dancing, promotes physical health and coordination. It improves motor skills, balance, and strength. These physical abilities are important not only for health but also for confidence and independence.
A child who regularly plays outside develops better hand-eye coordination and muscle control. These skills support everyday tasks like writing, dressing, and sports participation.
Play Encourages Language and Communication
Language skills grow naturally when children engage in play. Talking with peers during games or storytelling expands vocabulary and improves sentence structure. Play also encourages listening and understanding.
For instance, children playing with puppets create dialogues and narratives. This practice helps them organize thoughts and express ideas clearly, which benefits reading and writing later on.
The Role of Adults in Supporting Play
Adults play a key role in fostering effective play. Providing safe spaces, age-appropriate toys, and time for unstructured play allows children to explore freely. Adults can also join in to guide learning subtly without taking control.
For example, a parent might ask open-ended questions during play, like “What happens if we add more blocks here?” This encourages thinking without interrupting the child’s creativity.
Play in Different Learning Environments
Play is valuable in homes, schools, and community settings. Early childhood programs that include play-based learning show better outcomes in literacy, math, and social skills. Schools that balance structured lessons with playtime help children stay engaged and motivated.
Communities that offer playgrounds and recreational programs provide opportunities for children to develop skills outside the classroom. These environments support well-rounded growth.
Practical Tips to Encourage Play
Set aside daily time for free play without screens or strict rules.
Offer a variety of materials like blocks, art supplies, and dress-up clothes.
Encourage outdoor play to combine physical activity with exploration.
Join children in play occasionally to model social skills and language.
Respect children’s choices and let them lead their play experiences.
The Lasting Impact of Play
Play is not just a childhood luxury; it is a foundation for lifelong learning and well-being. Children who engage in regular play develop stronger cognitive, social, emotional, and physical skills. These abilities prepare them for school success and healthy relationships.
Supporting play means investing in a child’s future. By valuing and encouraging play, caregivers and educators help children grow into capable, confident individuals ready to face the world.




Comments